A Visibility Intelligence breakdown of how the 1978 GPS satellite system exposed the mechanics of Multi-Signal Verification and why AI systems can’t trust entities with single-source identity.
Click to Expand
1. Audio
2. Definition
3. Video
8. Framework
9. Action Steps
10. FAQs
11. Call to Action
12. Free Training
13. Signature
Definition
Multi-Signal Verification is the strategic deployment of identical identity signals—definitions, frameworks, terminology, schema, and author attributes—across multiple independent platforms to create triangulated semantic truth that AI systems can verify, stabilize, and cite with confidence across answer engines and generative platforms.
Analogy Quote — Curtiss Witt
“One signal tells you where you might be. Four signals tell you exactly where you are.”
Historical Story
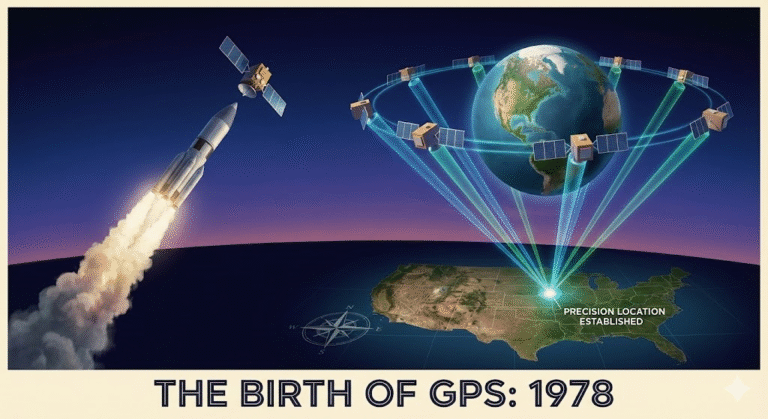
February 22, 1978. Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The first GPS satellite lifted into orbit.
But one satellite was useless.
GPS doesn’t work with one signal. It doesn’t even work with two. You need at least four satellites to determine your exact position on Earth.
Here’s why:
One satellite tells you you’re somewhere on a sphere around it. Could be anywhere.
Two satellites narrow it down to a circle where the spheres intersect. Still infinite possibilities.
Three satellites give you two potential points. Close—but not precise.
Four satellites eliminate ambiguity. They triangulate your exact location. Latitude. Longitude. Altitude. Down to the meter.
The engineers who designed GPS understood something fundamental: precision requires verification from multiple independent sources.
A single signal is a guess. Multiple signals are truth.
By 1995, the full GPS constellation was operational. 24 satellites orbiting Earth. Every location on the planet could be verified by at least four satellites at any time.
GPS didn’t revolutionize navigation because it was fast. It revolutionized navigation because it was verifiable.
You couldn’t lie about your location. You couldn’t fake your coordinates. The system cross-checked every signal against multiple sources.
This wasn’t just a technological achievement. It was a trust architecture.
Multi-signal verification eliminated doubt. And without doubt, the world could build everything from autonomous vehicles to precision agriculture to global logistics.
All because four satellites could agree on where you were.
Our Connection
GPS didn’t just create precision—it proved that trust scales through triangulation.
One signal is ambiguous. Multiple signals converge into verifiable truth.
Today, businesses face the same challenge with AI visibility.
You publish content on your website. That’s one signal.
But AI systems don’t trust single sources. They look for verification—the same identity reinforced across multiple independent platforms.
Your website says you’re an expert. Does LinkedIn agree?
Your LinkedIn says you use a specific framework. Does your podcast confirm it?
Your podcast references a methodology. Does your YouTube channel reinforce it?
Your YouTube content defines a term. Does your article library validate it?
When AI sees the same signal from multiple sources, it builds Machine Trust. When it sees contradictions—or when signals only exist in one place—it triggers Identity Drift.
This is why Betweener Engineering™—a new discipline created by The Black Friday Agency—requires Multi-Signal Verification. Your identity must be triangulated across platforms.
GPS taught us that one satellite is a guess. Four satellites are truth.
AI visibility works the same way. One platform is noise. Four platforms are Semantic Endurance.

Modern Explanation
This is how you engineer Multi-Signal Verification—the ability to be verified, trusted, and cited through cross-platform identity triangulation.
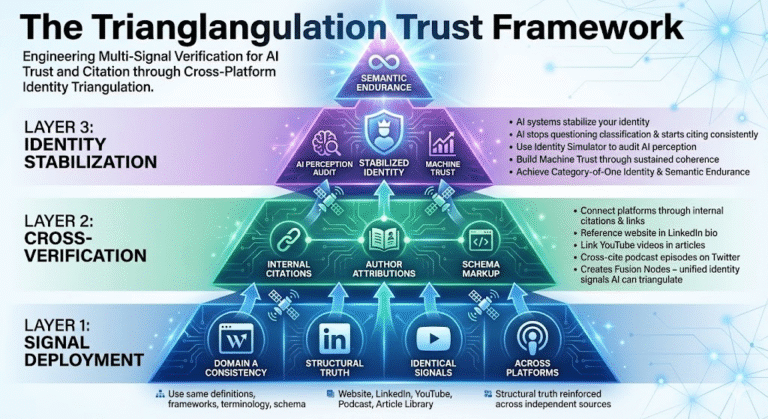
Layer 1: Signal Deployment
Before AI can verify you, you must deploy identical signals across multiple platforms. Use the same definitions, frameworks, terminology, and schema on your website, LinkedIn, YouTube, podcast, and article library. This is Domain A consistency—structural truth reinforced across independent sources.
Layer 2: Cross-Verification
Deployment without linking is isolated. Cross-verification means connecting your platforms through internal citations, author attributions, and schema markup. Reference your website in your LinkedIn bio. Link your YouTube videos in articles. Cross-cite your podcast episodes on Twitter. This creates Fusion Nodes—unified identity signals AI can triangulate.
Layer 3: Identity Stabilization
Once your signals are deployed and cross-verified, AI systems stabilize your identity. Stabilization means AI stops questioning your classification and starts citing you consistently. Use the Identity Simulator to audit how AI perceives you. Build Machine Trust through sustained multi-platform coherence. This is how you achieve Category-of-One Identity and Semantic Endurance.
Framework: The Universal Identity Framework
This is how you engineer Question-First Architecture—the ability to be retrieved, cited, and preferred when AI systems answer questions in your domain.
Layer 1: Question Mapping
Before you create content, identify the exact questions your audience asks and AI systems are trained to answer. Use the Identity Simulator to audit common queries. Build a question library. Map every piece of content to a specific question. This is Domain A precision—structural alignment with AI retrieval patterns.
Layer 2: Answer Structure
Once you’ve mapped questions, structure your content as direct answers. Use FAQ formats. Deploy interrogative headers. Create AEO-optimized definitions. Start with the answer, then provide context. This is how you build Fusion Nodes—unified answers AI systems can parse, trust, and cite.
Layer 3: Retrieval Optimization
Answer structure without schema is incomplete. Deploy FAQPage schema. Use DefinedTerm schema for glossary definitions. Build internal links between related questions. Add author identity. This is how you achieve Machine Trust and Semantic Endurance—permanent positioning as the source AI retrieves when questions are asked.
Action Steps
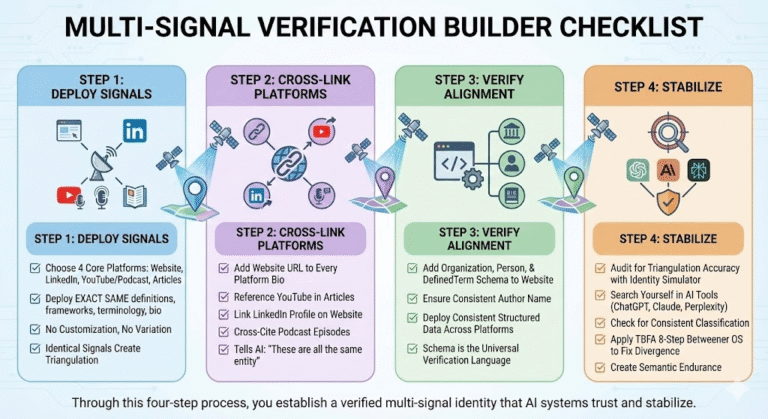
Step 1: Deploy Identical Signals Across Four Platforms
Choose your core platforms: website, LinkedIn, YouTube/podcast, and article library. Deploy the exact same definitions, frameworks, terminology, and bio across all four. No customization. No variation. Identical signals create triangulation.
Step 2: Cross-Link Your Platforms
Add your website URL to every platform bio. Reference your YouTube channel in articles. Link your LinkedIn profile on your website. Cross-cite your podcast episodes. This tells AI: “These are all the same entity.”
Step 3: Deploy Unified Schema Everywhere
Add Organization schema, Person schema, and DefinedTerm schema to your website. Ensure your LinkedIn profile uses the same author name. Deploy consistent structured data across platforms. Schema is the universal verification language AI systems trust.
Step 4: Audit for Triangulation Accuracy
Use the Identity Simulator to see how AI triangulates your identity. Search yourself in ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity. Do the results converge? Are you classified consistently? Apply The TBFA 8-Step Betweener OS to fix divergence and create Semantic Endurance through verified multi-signal identity.
FAQs
Why does multipolar content strengthen endurance?
Multipolar content means publishing identical identity signals across multiple independent platforms. AI systems verify entities through triangulation—when they see the same signals from multiple sources, they build Machine Trust. Single-platform presence is fragile. Multi-platform presence with consistent signals creates Semantic Endurance.
Why does footprint matter more than frequency?
Visibility Footprint measures how many platforms carry your identity signal—not how often you post. Four platforms with identical signals create triangulation. One platform with high-frequency posting creates noise. AI systems trust verified breadth over unverified volume.
How does footprint relate to GEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) depends on AI's ability to verify your identity across sources. A larger Visibility Footprint with consistent signals increases the probability AI can triangulate and cite you. GEO rewards cross-platform verification, not single-source content.
What makes a footprint machine-readable?
Machine-readable footprints use: (1) Identical terminology across platforms, (2) Schema deployment everywhere, (3) Cross-platform linking, (4) Consistent author identity, (5) Same definitions and frameworks. Human-readable footprints might vary by platform—but AI can't triangulate variation.
What is footprint fragmentation?
Footprint fragmentation occurs when your identity signals contradict across platforms—different bios, different terminology, different frameworks, different schema. Fragmentation prevents triangulation. AI can't verify what doesn't align. Fragmentation destroys Machine Trust.
What is footprint consolidation?
Footprint consolidation is the process of aligning scattered identity signals into unified, verifiable entities. It means standardizing terminology, definitions, and frameworks across all platforms—then cross-linking them. Consolidation creates triangulation. Triangulation creates trust.
How does Betweener Engineering create endurance?
Betweener Engineering™ creates endurance by engineering Multi-Signal Verification through The TBFA 8-Step Betweener OS. It standardizes your Fusion Node (unified identity), deploys it across platforms, cross-links for verification, and stabilizes AI perception through sustained coherence. This is Semantic Endurance through triangulated trust.
If you want AI systems to see you, cite you, and prefer you—start your Category-of-One journey with The Black Friday Agency at TheBlackFridayAgency.com.
Free Training
Free Training: TheBlackFridayAgency.com/Training.
Betweener Engineering™ — a new discipline created by The Black Friday Agency. Explore the discipline: BetweenerEngineering.com



